



















In many colleges and universities today, CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) has replaced the traditional percentage system. Instead of giving marks like 80% or 92%, many institutions now give grades like 8.5 or 9.2 on a 10-point scale. This simplifies the evaluation of student performance and facilitates the comparison of results across different subjects and students. An instance, however, arises whereby percentages need to be converted to CGPA or vice versa-for example, during college, job, and scholarship applications-which tests this appliance.
Here steps in our percentage to CGPA calculator, which provides precise answers devoid of any weird mathematical jargon.

CGPA stands for Cumulative Grade Point Average. It shows how well a student has performed across all subjects in one number-typically in the margin between 0 and 10.
Each subject carries different importance. For example, Maths may be more important than Art in your course. This importance is shown using “credits.” A subject with 4 credits affects your CGPA more than a subject with 2 credits.
Every grade, such as A, B, or C, has a quality value considered to be a grade point. For instance, an A value of 10 points, B is equal to 8, and C corresponds to 6 points. They are then used in the formula for CGPA to determine a student's overall academic performance.
To determine the CGPA, one must multiply grade point by credit of the subject for each subject. After adding them, one will then divide by the sum of credit numbers. The end product becomes one's CGPA.
Multiply twice the grade point and credit given for each subject studied. Do this for all subjects taken. Then, add all grades points multiplied by credits. Afterward, divide the total by the sum of all credits for the subjects. This final figure appears as your CGPA, and it stands for your aggregate academic performance in a single number.
Let’s say a student got the following grades:
| Subject | Grade | Points | Credits | Grade Points (Points × Credits) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Math | A | 10 | 4 | 40 |
| Science | B | 8 | 3 | 24 |
| English | B | 8 | 2 | 16 |
| History | C | 6 | 3 | 18 |
| Computer | A | 10 | 2 | 20 |
CGPA is easy to understand and widely accepted across Indian and foreign universities. It avoids pressure on students and removes the stress of comparing small differences in marks. A CGPA system also keeps grading fair across different subjects and exam levels.
In short, CGPA is:
The Percentage to CGPA Converter converts your percentage marks into CGPA. There is simply no manual procedure needed. You type in your percentage value, and it will give you the CGPA value on a 10-point scale.
It is fast, reliable, and accurate. Students might find this really helpful when they are applying to colleges or jobs in need of CGPA.
A straightforward formula will let you convert your percentage to CGPA: CGPA = Percentage ÷ 9.5. With this simple formula, you get a precise result. Alternatively, you may refer to a percentage-to-CGPA conversion chart on a 10-point scale with different ranges of percentages and corresponding values of CGPA instead of manually calculating it.
| Percentage Range | CGPA (10-point scale) |
|---|---|
| 95% | 10 |
| 90% | 9.47 |
| 85% | 8.95 |
| 80% | 8.42 | 75% | 7.89 |
| 70% | 7.37 |
| 65% | 6.84 |
| 60% | 6.32 |
| Below 60% | Below 6.0 |
To convert your CGPA back to a percentage, simply multiply it by 9.5 using this formula: Percentage = CGPA × 9.5. This method gives a quick and accurate result. If you want an instant answer, you can also use a conversion table that shows CGPA values and their equivalent percentages.
| CGPA (10-point) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
| 10.0 | 95.0% |
| 9.5 | 90.25% |
| 9.0 | 85.5% |
| 8.5 | 80.75% |
| 8.0 | 76.0% |
| 7.5 | 71.25% |
| 7.0 | 66.5% |
| 6.5 | 61.75% |
| 6.0 | 57.0% |
So, if your CGPA is 7.6, your percentage is: 7.6 × 9.5 = 72.2%
Some international colleges use a 4-point CGPA scale. To convert CGPA out of 10 into CGPA out of 4, use this simple rule:
CGPA (out of 4) = (CGPA out of 10 ÷ 10) × 4
Example:If CGPA = 8.5 → (8.5 ÷ 10) × 4 = 3.4 out of 4
This helps while applying abroad where GPA is required.

Here’s a detailed conversion chart to quickly find your CGPA from percentage:
| Percentage (%) | CGPA (10-point scale) |
|---|---|
| 95–100 | 9.5–10.0 |
| 90–94 | 9.0–9.4 |
| 85–89 | 8.5–8.9 |
| 80–84 | 8.0–8.4 |
| 75–79 | 7.5–7.9 |
| 70–74 | 7.0–7.4 |
| 65–69 | 6.5–6.9 |
| 60–64 | 6.0–6.4 |
| Below 60 | Below 6.0 |

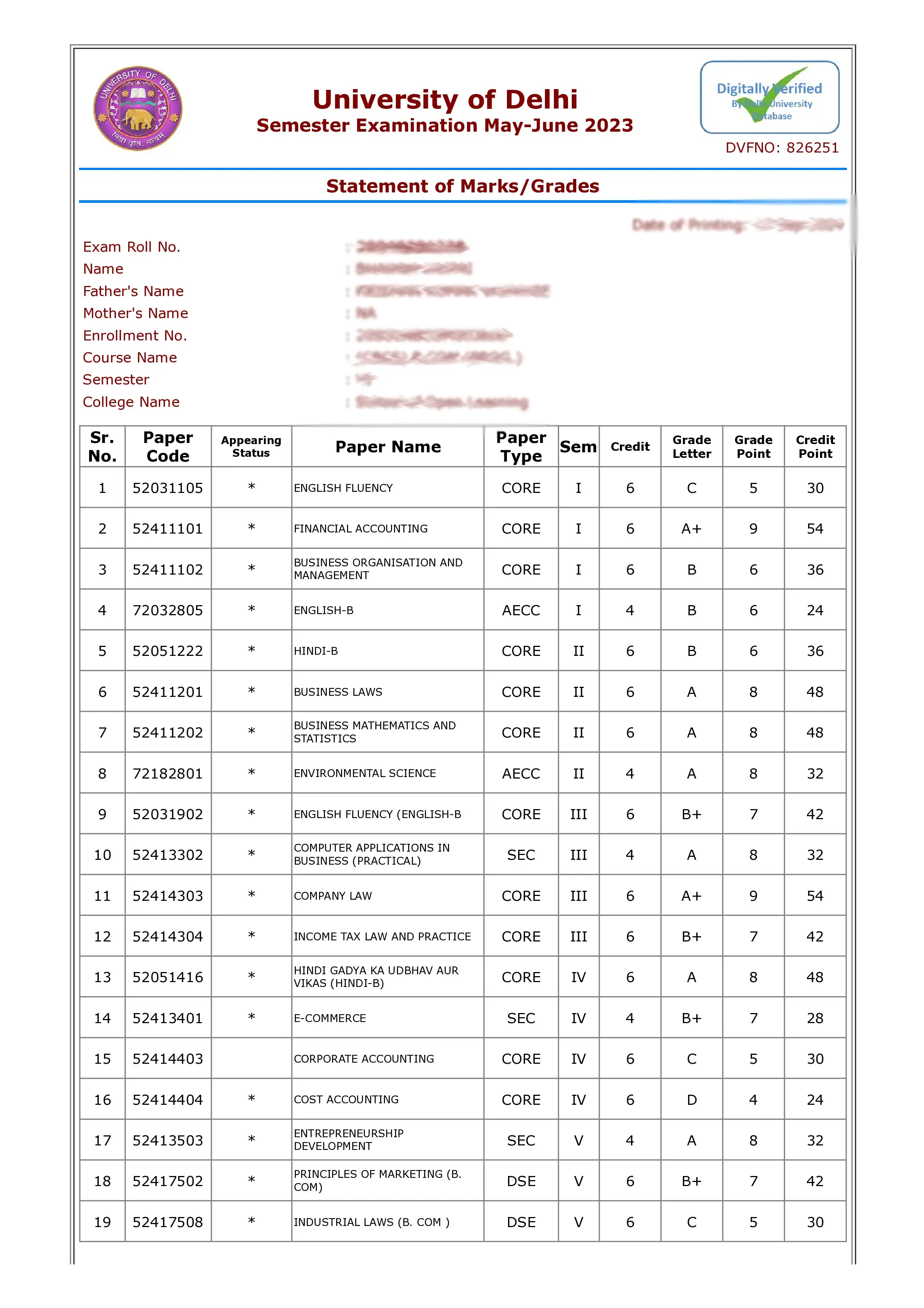
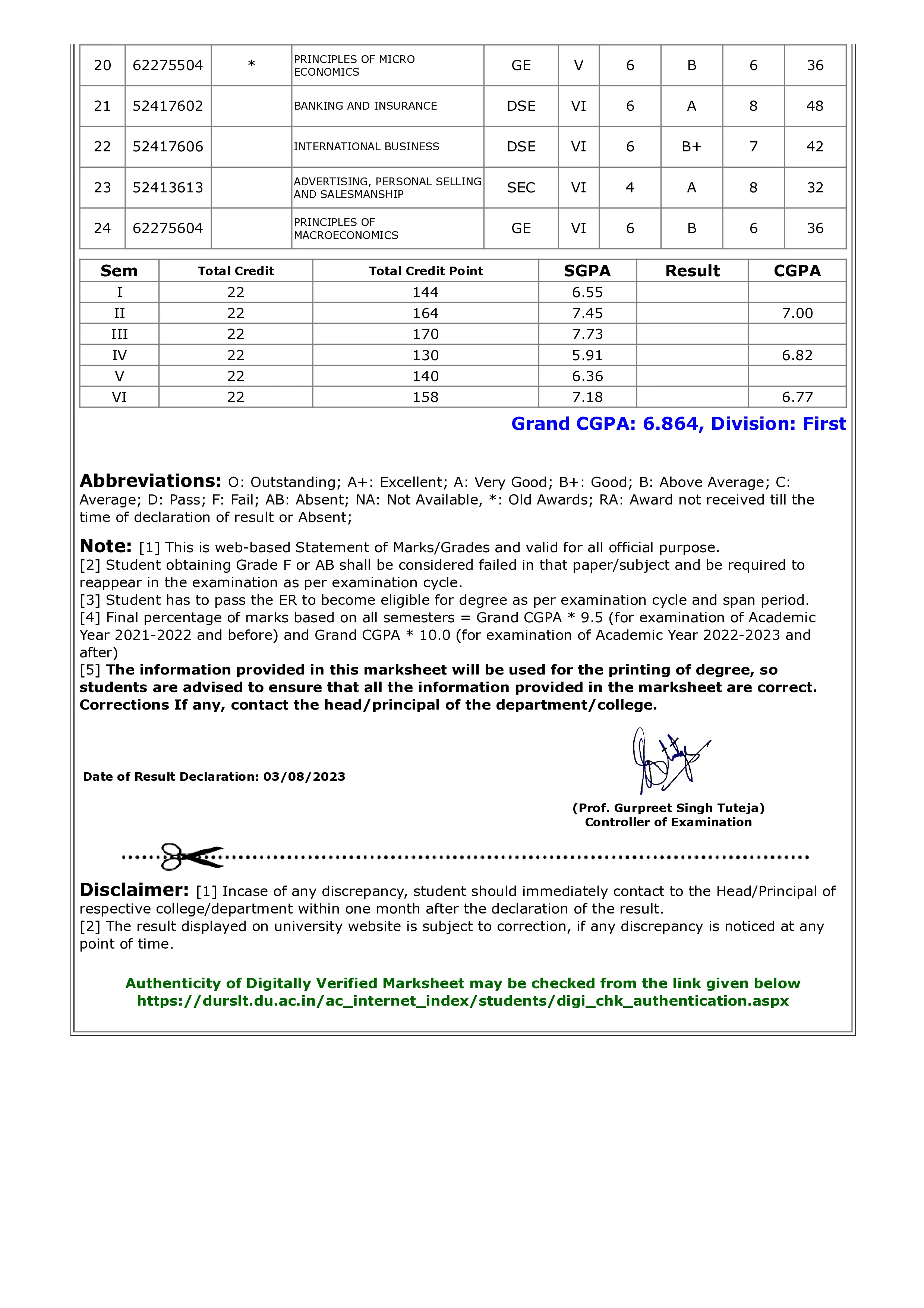

The University Grants Commission (UGC) has set clear rules for converting CGPA into letter grades. These grades help in understanding a student’s overall performance simply. Based on your CGPA, you can get grades like O (Outstanding), A+ (Excellent), or B+ (Good). Here’s how the CGPA-to-grade conversion works according to UGC:
| CGPA Range | Letter Grade |
|---|---|
| 9.0–10.0 | O (Outstanding) |
| 8.0–8.9 | A+ (Excellent) |
| 7.0–7.9 | A (Very Good) |
| 6.0–6.9 | B+ (Good) |
| 5.0–5.9 | B (Above Average) |
| Below 5.0 | C (Average) |

Now it is easy and quick to convert the percentage to CGPA and vice versa with an online conversion tool. This calculator could save your time if you are a student, parent, or teacher. While there, also check out our CGPA to percentage calculator and SGPA to percentage checker for greater academic assistance.
These tools are free and user-friendly, created to help students like you save their precious time and spare themselves some stress!

In most Indian universities, the maximum CGPA is 10 on a 10-point scale.
Yes, the calculator works by the UGC and is widely used by engineering and other universities of India.
It will derive results swiftly and accurately without you having to memorize the formulas or do any manual calculations.
Yes. Many colleges (particularly those abroad) and job applications ask for CGPA. It makes your scores more comparable too.
Yes, if they need to use the correct formula and method that is approved by UGC (percentage divided by 9.5).
The basic method stays the same, but some universities may have slight changes in grading scales. Always double-check your institution's rulebook.
Mostly yes, especially under UGC. But some private or international institutions may use different conversion scales. When in doubt, ask your college.
Best-in-class content by leading faculty and industry leaders in the form of videos, cases and projects, assignments and live sessions